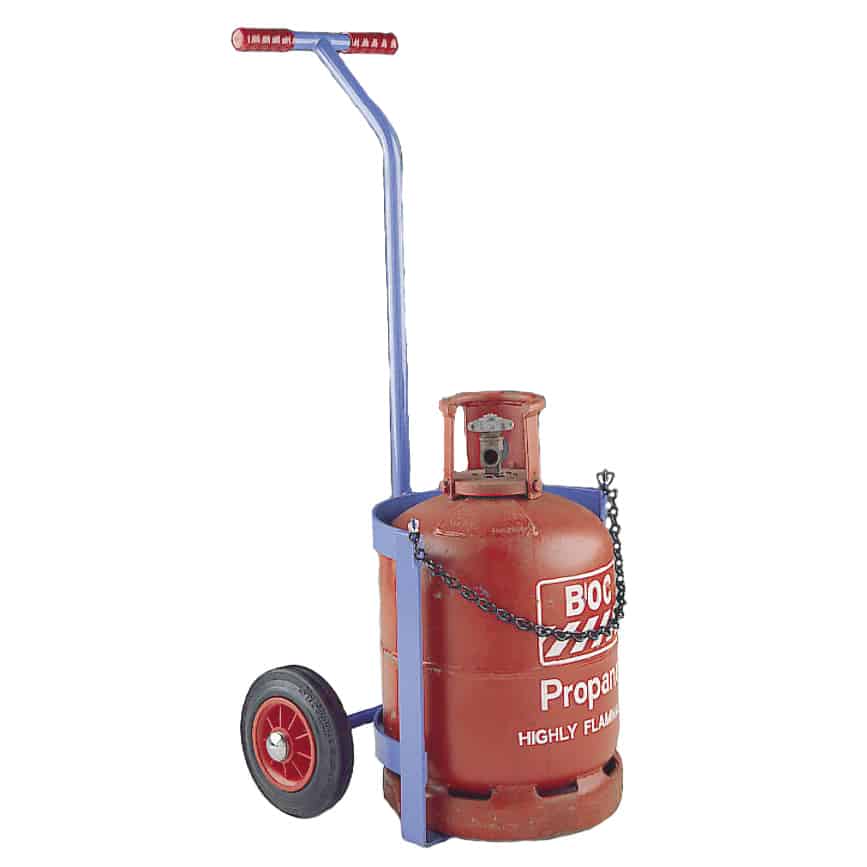
Storing gas requires a compressed gas cylinder, which is a type of steel vessel that will keep the gas densely stored in a gas bottle without the possibility of a leak. The tight seal of the cylinder is due to special cylinder valves, which allow for the controlled release of gas in precise amounts.
A gas cylinder is typically long and has a valve at the top, with most of them having flat bottoms to help place them upright. Gas cylinders have the following features to help them store the gas:
- Strong cylinder materials: Because the storage is at higher levels than atmospheric pressure, there is need for a strong container materialn, most often steel. They will need to be unwelded and corrosion-resistant to prevent weak points on a gas bottle.
- Cylinder valves: The valves expel the gas slowly when released, but their main role is to act as a control point for the pressure on the inlet and outlet port. Cylinder valve types include O ring valves, diaphragm valves, packed valves and pressure seal valves.
- Gas regulators: The pressure in the cylinder, not the volume of gas, is indicated by a regulator near the valve. Regulators have dials and are used when refilling gas, which is achieved using a bigger tank that comes directly from a gas processing plant.
We sell many types of gas cylinder storage products for LPG and other gas bottles, which are available with free UK delivery, so we are well-placed to explain a bit more about how they work.
Please feel free to browse our range of gas storage products and buy online or get in touch with us if you have any product questions. You can read on to learn more about gas cylinders.
How LPG Cylinders Work
LPG stands for ‘liquefied petroleum gas’, so an LPG cylinder is simply a container for this type of substance. An LPG might be used as fuel for heating or cooking, as a propellant or refrigerant – or in many other industrial applications. Many people commonly use them for barbecues.
They work in essentially the same way as every other type of gas cylinder, but the contents of an LPG cylinder are compacted to the point that the vapour in the gas becomes a liquid while in the cylinder. Releasing the valve creates an exit point, where the vapour becomes aerosolized.
This is in contrast to many more conventional gas cylinders, such as those containing oxygen or nitrogen, which are simply compressed gas (with no liquid) that is released from the valve.
‘Petroleum gas’ is a bit generic, but people who use the term typically refer to propane or butane, although sometimes a mixture is used too. Other petroleum gases include propylene.

How Long Does a Gas Cylinder Last?
A gas cylinder can come in a wide range of different sizes, so there is no set amount of time that it will last in terms of running out of capacity. Certain gases can be stored more densely, and liquefied vapour can often be stored at many times the capacity of the bottle.
However, all gas cylinders have a lifespan. As a result, you can only refill a cylinder and feed it into an apparatus a certain number of times. Again, there is no set time frame, but certain types of cylinder materials can work for up to 70 years. Repairs, valve replacements and maintenance help to increase the average cylinder lifespan.
Regular inspections will determine how long a cylinder is safe to use, but this is only normally necessary every 5 years. Factors that affect the lifespan of a gas cylinder include the following:
- Cylinder material, steel is very robust while fibre materials may weigh less but not last as long
- Type of use, oxygen cylinders for diving might be affected by salt corrosion and cylinders with heavy use or transport requirements may become damaged
- Corrosion, which may occur from exposure to various substances, due to damage and with the effects of age
There are limits to any kind of pressure vessel, even huge industrial tanks in gas power plants, but their construction means they can last an exceptionally long time in the right conditions.
Are Gas Cylinders Safe?
High-pressure cylinders are generally safe, but they can also contain many potentially hazardous substances, such as carbon dioxide, propane or butane and others. However, the pressure within the container can also present a danger in itself – even if it contains a harmless substance.
Potential dangers of poor gas cylinder handling or use include the following:
- Fire or explosion, certain substances including oxygen can set alight easily – exploding valves and tanks can also catapult shrapnel around a space
- Valve breakage, a broken valve on a gas cylinder can sometimes cause it to become a projectile and fly around uncontrolled – this may be a potentially fatal accident
- Gas leaks, certain gases can reduce the level of oxygen in the air and can potentially cause harm to health, or even death, if they are inhaled
- Physical hazards, such as toppling or crushing – as some gas cylinders are very heavy due them containing extremely high densities of gas
Cylinders should only be handled, emptied or used with the proper guidance and training in the workplace and domestic gas cylinders should be inspected and refilled by a professional. Do not tamper with or try to repair a leaking cylinder without supplier assistance.
A few simple safety tips for handling gas cylinders include the following:
- Avoid dropping, throwing or moving cylinders without due care
- Use personal protective equipment if you are refilling a gas cylinder
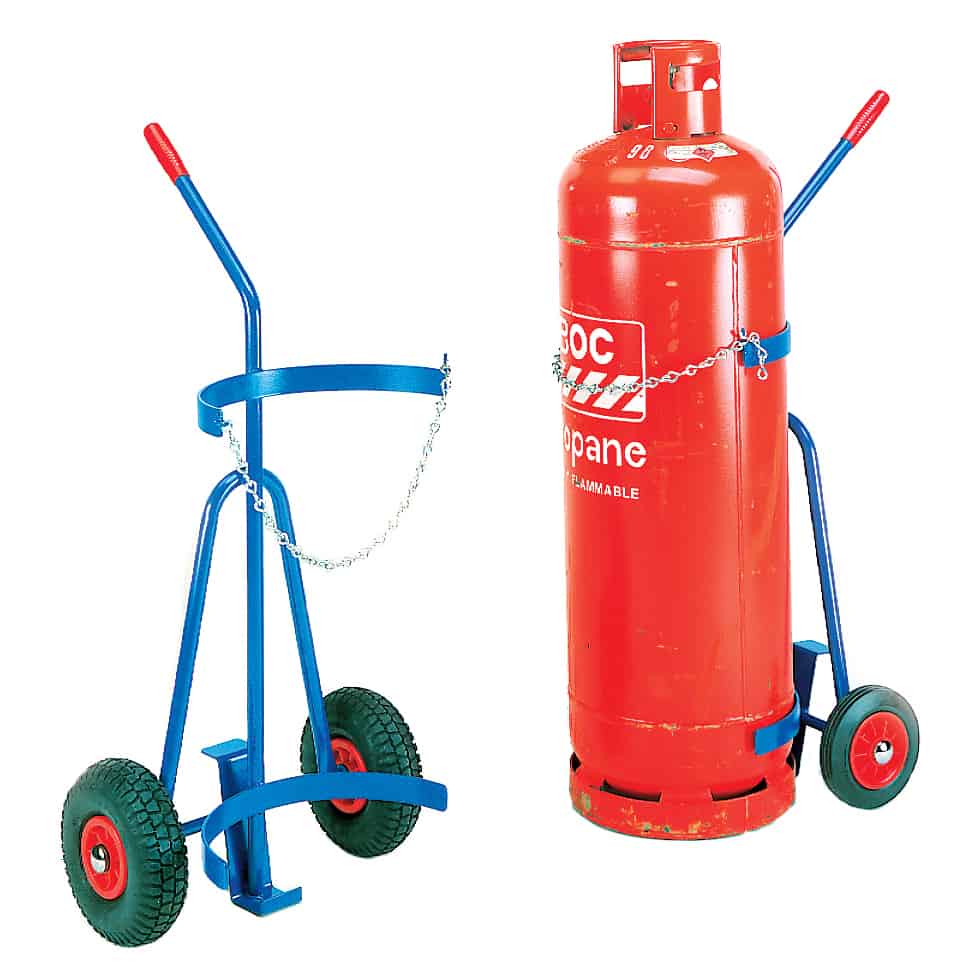
- Fasten cylinders using a chain or other protective guard when in use
- If moving cylinders in a vehicle, always travel with an accessible fire extinguisher
- After using and before moving a cylinder, check that all of the valves are sealed
- Do not smoke or use any other type of naked light near a gas cylinder

There are many authorities and safety standard enforcement agencies in different countries throughout the world. In the United Kingdom, gas cylinder safety falls under the authority of the Health and Safety Executive (HSE).
How Should You Store Gas Cylinders?
Whether you have your own cylinder of propane for an outdoor barbecue, use oxygen cylinders for diving, work with other compressed gases or anything else, the HSE has some guidelines for storage. The HSE’s gas cylinder storage guidelines include the following:
- Store upright, with the valve always situated at the top
- Preferably keep them outside, or in another well-ventilated area
- Place cylinders in a cage, or other secure space on a concrete or load-bearing floor
Gas cylinders should also always be kept away from potentially corrosive substances, such as strong acids and cleaning chemicals, flammable substances and anything else that can potentially compromise the integrity of the vessel.
How Gas Cylinders Work Explained
We hope you understand a little bit more about how gas cylinder storage systems work and the potential uses they have. With a large array of different contents, the substances can range from relatively harmless, such as oxygen, or potentially dangerous, such as carbon dioxide or LPG gas.
Gas cylinders work by compressing the gas above atmospheric pressure, which will vary depending on the gas, and are controlled by a valve system and gas regulator.
Buy Heavy-Duty Gas Cylinder Storage
To safely store your gas cylinders you can use our high-quality gas storage products, which are perfect for commercial and industrial settings and also come with free UK-mainland delivery.
Please feel free to get in touch with us if you have any questions about any of our products.